Meeting Productivity Consultants
Transform your meeting culture
MeetingFever consulting offers strategic advice for fewer, more efficient meetings across your whole organisation in the age of remote work. Learn how to reduce meeting time and sign up for our free webinar.
Communication becomes complex when teams grow...
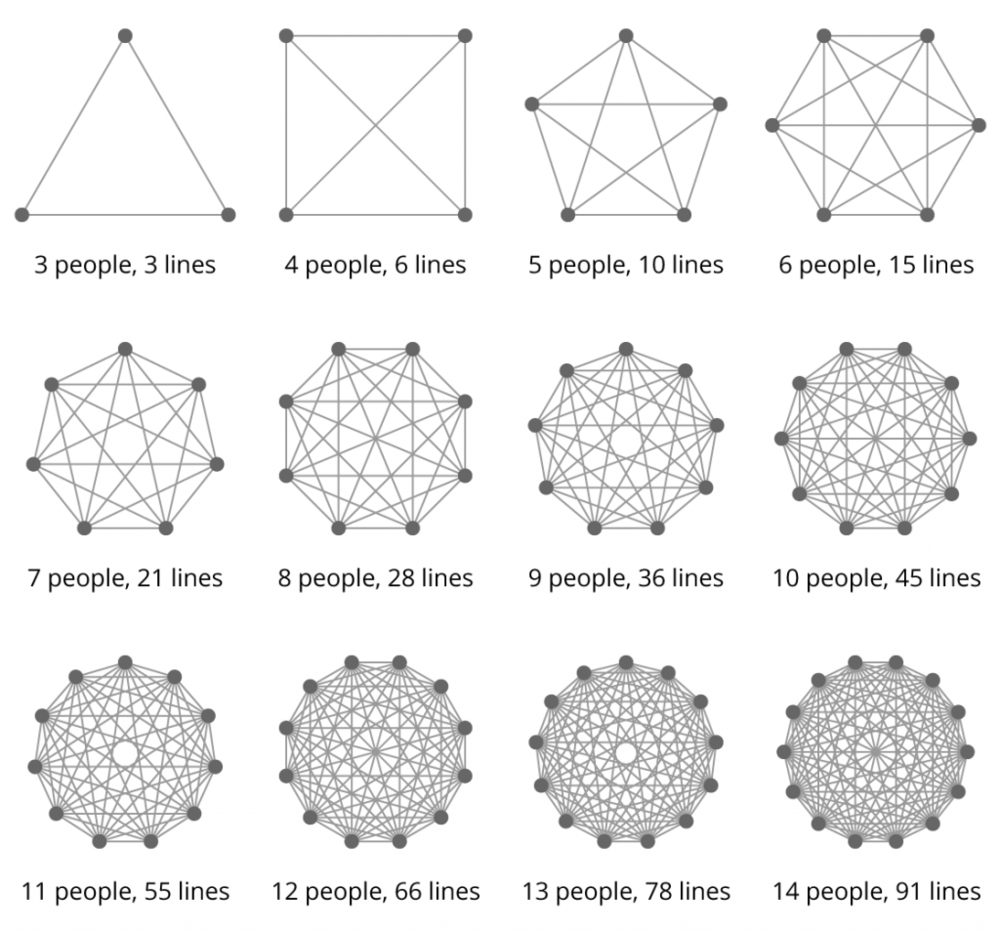
When startups scale, communication among team members and across departments often fails. Too many lines of communication have to be managed, and when left unchecked, meetings become an end in themselves instead of a means to move work forward.
Avoid meeting creep by adopting a battle-tested meeting management framework, which ensures meeting time is cut down and employee productivity soars.
Stop being enslaved by your meeting procedures and implement modern meeting guidelines across your entire organization with our help.
It's time to make your company's meetings more efficient
$399 Billion Lost Annually
U.S. businesses lose this due to poorly organized meetings.
31 Hours Spent Monthly
Average time employees spend in unproductive meetings.
When you look at these numbers, you’ll realize that something is wrong with our meetings. Too often, meetings are characterized by the following negative points:
- Unprepared participants
- Inefficient meeting preparation
- Too many scattered documents
- Too many different tools
- No buy-in
- Endless discussions
Yet, this doesn’t have to be the case. Meetings are a central and crucial component for any organization. However, meetings require structure and must be utilized correctly. We’ll show you how it’s done.
Your Go-To Resource
For Meeting Productivity
We write about meetings from different perspectives. Our content will help you, no matter what position you are in.
I Am A Business Owner And I Want To Improve The Meetings In My Company
Are you an entrepreneur or a business owner and want to increase the productivity of meetings in your company?
- Available Soon -
I Am A Manager And I Want To Improve The Meetings In My Team
Do you lead a team and want to improve the meeting workflow in your team? We've created a guide for you.
I Am An Employee And I Want To Improve My Meetings
Are you an employee and have a problem with too many and inefficient meetings?
- Available Soon -
About Us
We are Florian, Jannik, and Alexander, founders, tech enthusiasts, and online marketers.
In 2016, we launched our first media company, fueling our passion for optimizing work life. In 2023, we started a new venture, ZipDo, a productivity software firm. Through MeetingFever, we aim to share our productivity tips and routines with you.
Our Meeting Lifecycle Concept
We write extensively on this page about the meeting process. When we were dissatisfied with our own meetings in our first company, we studied all available resources on meetings and developed the Meeting Lifecycle for ourselves. We describe this principle in detail on this page.
Before the meeting, it’s crucial for all participants to prepare, gather, and distribute relevant documents. The necessity of the meeting should also be evaluated at this stage. A meeting agenda should be created and made accessible to all participants.
During the meeting, notes should be taken. The meeting’s moderator must ensure adherence to the agenda.
Archive your meeting notes or retrieve valuable information from previous meeting notes and enable users to quickly find, share and export critical knowledge.
Our Meeting Resources
Meeting Templates
Use our free meeting templates to kickstart your meetings.
Meeting App Reviews
Use our free meeting templates to kickstart your meetings.
Meeting Guides
Use our free meeting templates to kickstart your meetings.
Modern Work Statistics
We've collected some recent data about meetings and modern work.
Our Meeting Software
Discover our bootstrapped meeting notes software Zipdo and try it free.
Meeting Facilitation Training
We've created a training program for managers and team leaders.
Questions? Don't hesitate, contact us!
Do you have a question, idea, proposal or anything you would like to discuss? Then send us a quick message. We typically reply in 24 hours.
FAQs
What is MeetingFever?
MeetingFever is a digital training platform & consultancy provider for better and more efficient meetings. We offer a free 7-day email newsletter that teaches you the basics of efficient team meetings.
How do we make money?
MeetingFever is a content platform dedicated to the topic of efficient meetings. We are the founders of a meeting notes software, ZipDo, and have spent a considerable amount of time in our company focusing on meeting effectiveness. On MeetingFever.com, we share our insights and demonstrate to other companies how they can make their meetings more efficient.
What is ZipDo?
ZipDo is our Meeting Software, that we’ve developed based on our experience with meetings. Our content is designed to help all users improve their meetings. From time to time we describe how you can improve your meeting processes with our software; this type of monetization allows us to finance content creation.